Setting up a MySQL to S3 Pipeline with Vanus
Get notifications from Mysql to your s3 bucket
Welcome to my article on MySQL to S3 pipeline using Vanus! In this post, we’ll explore how you can set up a reliable and scalable pipeline to export data from your MySQL database to Amazon S3 using Vanus, a powerful data integration platform.
If you’re using MySQL to store critical data for your business, it’s important to ensure that you have a backup and archiving solution in place. Storing data in S3 provides many benefits, including durability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. With Vanus, you can easily set up a pipeline to extract data from your MySQL database and write it to S3.
By the end of this blog post, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to set up a MySQL to S3 pipeline using Vanus, and you’ll be equipped with the tools and knowledge you need to ensure that your data is backed up and archived in a reliable and scalable manner. So let’s dive in!
Using Vanus, we can automatically send customized messages to multiple email recipients without a single line of code.
Table of content
Step 1: Deploy Vanus on the Playground
Step 3: Deploy the S3 Sink Connector
About Amazon s3
What is Amazon s3?
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a cloud-based object storage service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). S3 provides a scalable and secure way to store and retrieve data from anywhere on the internet. It is designed to be highly available and durable, with an SLA that promises 99.999999999% (11 nines) of object durability.
S3 enables users to store and retrieve any amount of data, from anywhere in the world, through a simple web interface, APIs or AWS CLI. S3 stores data as objects, which are organized into buckets. A bucket is a container for objects, and you can think of it as a folder in a file system. Each object in S3 has a unique key, which identifies the object within the bucket.
S3 supports various features such as versioning, lifecycle policies, access control, security and compliance, and data transfer acceleration. S3 can also integrate with other AWS services such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), AWS Lambda, AWS Glue, and more, to build powerful data processing and analysis pipelines.
S3 is widely used for a variety of use cases such as data backup and archive, big data analytics, media storage and distribution, and mobile and web application hosting, among others. S3 offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which makes it a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
Backup with Amazon S3?
There are several reasons why you should backup your MySQL database into Amazon S3:
Durability and availability: Amazon S3 is designed to provide highly durable and available storage for your data. S3 stores data in multiple locations and automatically replicates data across different availability zones to ensure that your data is highly available and protected against data loss.
Scalability: S3 provides unlimited storage capacity, which means that you can store as much data as you need. You can easily scale up or down your storage capacity based on your business needs, without having to worry about provisioning additional hardware or managing complex storage infrastructure.
Cost-effectiveness: S3 offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which means that you only pay for the storage you use. This makes it a cost-effective solution for backing up your MySQL database, especially if you have large amounts of data to backup.
Easy access and retrieval: S3 provides a simple web interface, APIs and AWS CLI to access and retrieve your data from anywhere in the world. This means that you can easily retrieve your data in case of a disaster or data loss event.
Data processing and analysis: S3 can integrate with other AWS services such as AWS Glue, Amazon Athena, Amazon Redshift, and more, to build powerful data processing and analysis pipelines. This means that you can leverage the power of these services to process and analyze your data in the cloud, without having to manage your own data infrastructure.
Overall, backing up your MySQL database into Amazon S3 provides a reliable and scalable solution for protecting your critical data, while also enabling you to leverage the power of AWS services to process and analyze your data in the cloud.
Business scenario
Disaster Recovery: By backing up your MySQL database to Amazon S3, you can ensure that your data is protected in case of a disaster or data loss event. You can restore your data from S3 to a new database instance in case your original database becomes unavailable or corrupted.
Long-term data archiving: Amazon S3 is a cost-effective solution for long-term data archiving. You can use MySQL to S3 pipeline to regularly backup your historical data to S3 and easily retrieve it when needed.
Analytics and reporting: By using AWS services such as Amazon Athena, Amazon Redshift, or AWS Glue, you can analyze and report on your MySQL data that is stored in S3. This scenario is particularly useful if you have large volumes of data that are difficult to analyze within your MySQL database.
Data Warehousing: If you are using AWS Redshift as your data warehouse solution, you can use the MySQL to S3 pipeline to load data into Redshift from S3. This allows you to centralize your data in Redshift and use it for business intelligence and data analytics.
Data Backup and Recovery: You can use the MySQL to S3 pipeline to backup and restore your MySQL data. You can set up a schedule to regularly back up your data to S3 and quickly restore it in case of data loss.
DevOps: If you are running a MySQL database in your development or testing environment, you can use the MySQL to S3 pipeline to copy the database from your production environment to your development or testing environment. This ensures that your development or testing environment is up-to-date with the latest data.
GDPR compliance: If you are subject to GDPR regulations, you can use the MySQL to S3 pipeline to anonymize or pseudonymize your data before storing it in S3. This helps you to comply with GDPR regulations that require you to protect the privacy of your customers.
Cost-effective data storage: Amazon S3 is a cost-effective solution for storing large volumes of data. You can use the MySQL to S3 pipeline to move infrequently accessed data to S3 and save costs on storage.
Pre-requisite
Have a MySQL Database
Have An AWS account
Send customized event from Mysql to S3
The following are the three steps for setting up a MySQL to S3 pipeline using Vanus:
Deploy Vanus: The first step is to Deploy Vanus, an open-source event streaming platform in Kubernetes.
Start MySQL connector: After Deploying Vanus, you need to configure and start the MySQL connector.
Start S3 connector: Once the MySQL connector is running, you can configure and start the S3 connector.
By following these three steps, you can set up a MySQL to S3 pipeline using Vanus and begin copying your data from MySQL to S3. Once the pipeline is set up, you can automate the data transfer process and customize it according to your specific business needs.
Step 1: Deploy Vanus on the Playground
Go to Vanus Playground, and click “Continue with GitHub”
Wait until the K8s environment is ready (usually less than 1 min).
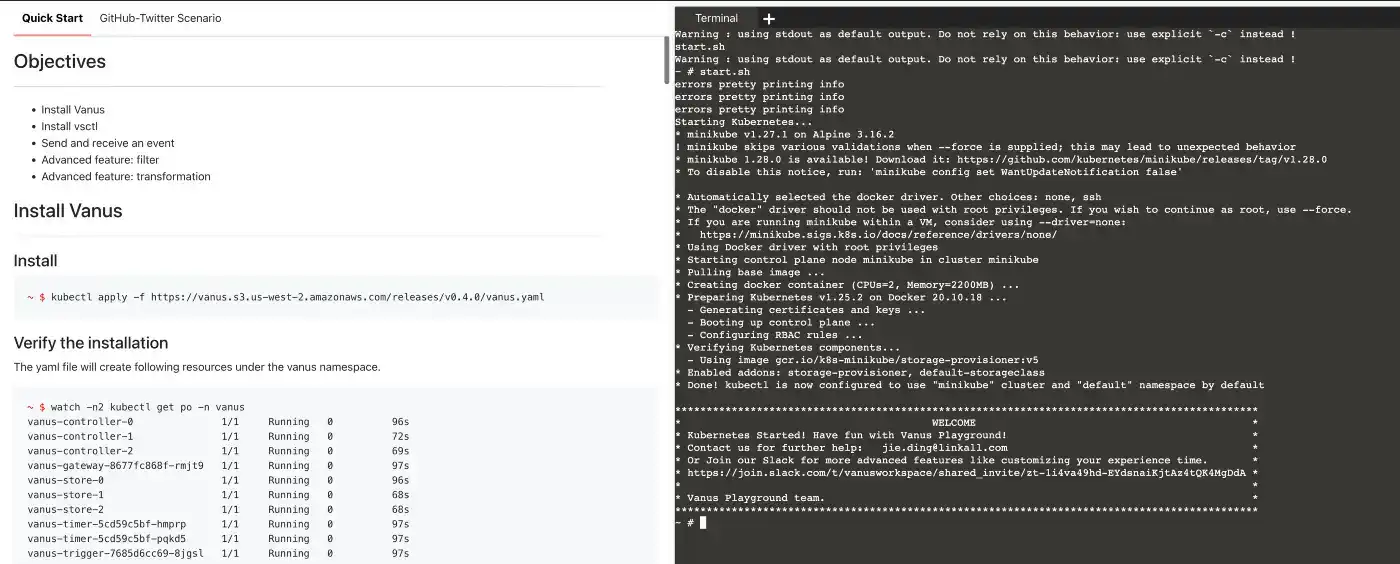
Install Vanus by typing the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://download.linkall.com/all-in-one/v0.6.0.ymlVerify if Vanus is deployed successfully:
$ watch -n2 kubectl get po -n vanus vanus-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 96s vanus-controller-1 1/1 Running 0 72s vanus-controller-2 1/1 Running 0 69s vanus-gateway-8677fc868f-rmjt9 1/1 Running 0 97s vanus-store-0 1/1 Running 0 96s vanus-store-1 1/1 Running 0 68s vanus-store-2 1/1 Running 0 68s vanus-timer-5cd59c5bf-hmprp 1/1 Running 0 97s vanus-timer-5cd59c5bf-pqkd5 1/1 Running 0 97s vanus-trigger-7685d6cc69-8jgsl 1/1 Running 0 97s
Install vsctl (the command line tool).
curl -O https://download.linkall.com/vsctl/latest/linux-amd64/vsctl chmod ug+x vsctl mv vsctl /usr/local/bin
Set the endpoint for vsctl.
export VANUS_GATEWAY=192.168.49.2:30001
Create an Eventbus to store your events.
$ vsctl eventbus create --name mysql-s3-scenario +----------------+---------------------+ | RESULT | EVENTBUS | +----------------+---------------------+ | Create Success | mysql-email-scenario| +----------------+---------------------+
Step 2: Deploy the MySQL Source Connector
Enable binary logging if you have disabled it (MySQL default Enabled). Create a new USER and grant roles, choose a unique password for the user.
CREATE USER 'vanus'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'PASSWORD'; GRANT SELECT, RELOAD, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON . TO 'vanus'@'%';
Create the config file for MySQL in the Playground. Change MYSQL_HOST, MYSQL PORT, PASSWORD, DATABASE_NAME, and TABLE_NAME.
cat << EOF > config.yml target: http://192.168.49.2:30002/gateway/mysql-s3-scenario # Vanus in Playground name: "quick_start" db: host: "MYSQL_HOST" # IP address of MySQL server port: MYSQL PORT # port address of MySQL server username: "vanus" # Username password: "PASSWORD" # Password previously set database_include: [ "<DATABASE_NAME>" ] # The name of your database # format is vanus_test.tableName table_include: [ "TABLE_NAME" ] # The name of your Table store: type: FILE pathname: "/vanus-connect/data/offset.dat" db_history_file: "/vanus-connect/data/history.dat" EOF
Run MySQL Source in the background
docker run -it --rm --network=host \ -v ${PWD}:/vanus-connect/config \ -v ${PWD}:/vanus-connect/data \ --name source-mysql public.ecr.aws/vanus/connector/source-mysql &Step 3: Deploy the S3 Sink Connector
To generate the YAML file for launching the S3 Sink connector in Kubernetes, execute the command provided bellow.
cat << EOF > s3-sink.yml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: sink-aws-s3 namespace: vanus spec: selector: app: sink-aws-s3 type: ClusterIP ports: - port: 8080 name: sink-aws-s3 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: sink-aws-s3 namespace: vanus data: config.yml: |- port: 8080 aws: access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE secret_access_Key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY region: "us-west-2" bucket: "mybucket" scheduled_interval: 10 --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: sink-aws-s3 namespace: vanus labels: app: sink-aws-s3 spec: selector: matchLabels: app: sink-aws-s3 replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: sink-aws-s3 spec: containers: - name: sink-aws-s3 image: public.ecr.aws/vanus/connector/sink-aws-s3 imagePullPolicy: Always ports: - containerPort: 8080 name: http volumeMounts: - name: config mountPath: /vanus-connect/config volumes: - name: config configMap: name: sink-aws-s3 EOFYou can edit the configuration settings by opening the “s3-sink.yml” file in the vi text editor using the command “vi s3-sink.yml”. Once the file is opened in the editor, you can make any necessary modifications to the configuration parameters and save the changes before exiting the editor.
aws.access_key_id
aws.secret_access_key
region
bucket
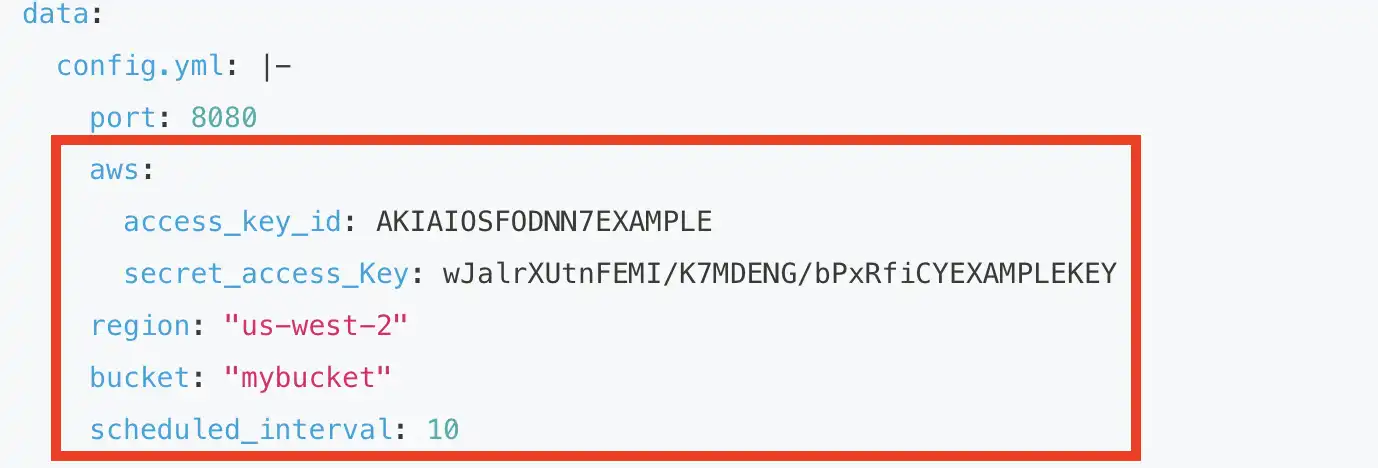
vi s3-sink.yml
How to exit.
ESC Shift + : wq Enter
Run AWS S3 Sink in Kubernetes
kubectl apply -f s3-sink.yaml
Check out the results
Here is a short recap of the three steps involved in setting up a MySQL to S3 pipeline using Vanus:
Step 1: Deploy Vanus - Using the playground to install Vanus in Kubernetes.
Step 2: Start MySQL Connector - Configure and start the MySQL connector by providing the necessary database connection details, such as the hostname, port, username, and password, and configuring any necessary data filters.
Step 3: Start S3 Connector - Configure and start the S3 connector by providing the S3 bucket details, such as the bucket name and region, and configuring any necessary data transforms.
To connect the Vanus Eventbus to the S3 Sink, you will need to create a subscription that specifies the Eventbus and the target Sink. This can typically be done via the Vanus command line vsctl.
Here is the command to create a subscription:
vsctl subscription create \ --name quick-start \ --eventbus mysql-s3-scenario \ --sink 'http://sink-aws-s3:8080'Learn more about the Subscription specifications for filtering and Transformation here.
Let’s test everything by making an entry in MySQL.
INSERT into DATABASE.TABLE values();
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pipeline from MySQL to AWS S3 using Vanus is an efficient and streamlined solution for storing and managing data. The use of Vanus allows for easy integration with various cloud services and APIs, making it an ideal choice for developers and data analysts alike. By leveraging the power of Vanus, organizations can improve their data management and analysis capabilities, ultimately leading to better business outcomes. With the right implementation and configuration, this pipeline can unlock a wealth of insights from the data generated by MySQL databases.
241
0
0

Comments
All Comments (0)