What is electric gate valve?
In the realm of fluid control systems, valves play a critical role in managing the flow of liquids or gases. Electric gate valves represent a technologically advanced and efficient solution for regulating fluid flow in various industrial applications. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of electric gate valves, exploring their design, functionality, and applications across different industries.
Understanding Gate Valves:
Gate valves are a type of linear motion valve used to control the flow of fluid through a pipe or duct. They are characterized by a gate or wedge-shaped disc that can be lifted or lowered into the flow path to either allow or block the passage of fluid. Gate valves are widely employed in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing due to their ability to provide a tight seal and low fluid resistance.
Electric Gate Valves: The Technological Leap:
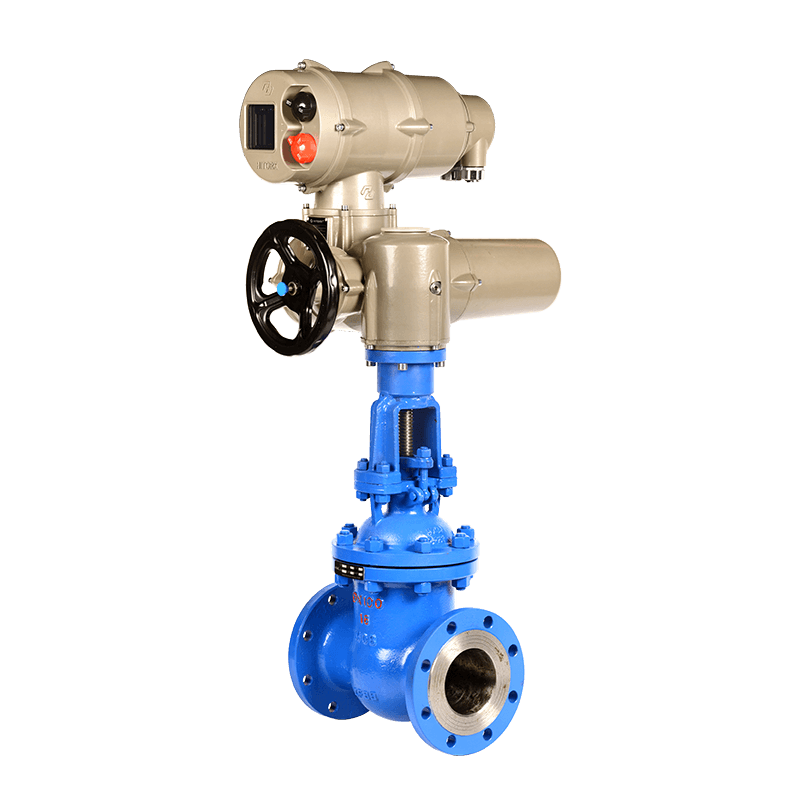
Electric gate valves, as the name suggests, are gate valves that are equipped with electric actuators for automated control. The addition of electric actuators eliminates the need for manual operation, providing a more efficient and precise means of regulating fluid flow. These electric actuators can be controlled remotely, making them suitable for applications where automation, accuracy, and remote operation are crucial.
Key Components of Electric Gate Valves:
a. Actuator: The electric actuator is the heart of an electric gate valve. It is responsible for opening and closing the valve by converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. Electric actuators offer the advantage of precise control and automation.
b. Gate or Wedge: The gate or wedge is the movable component that controls the flow of fluid. In the case of electric gate valves, the gate is manipulated by the electric actuator to either permit or restrict the passage of the fluid.
c. Stem: The stem is the component that connects the gate to the actuator. It transmits the motion generated by the actuator to the gate, allowing for smooth and controlled valve operation.
Advantages of Electric Gate Valves:
a. Automation: The primary advantage of electric gate valves is their automation capabilities. They can be remotely controlled, allowing for precise and efficient management of fluid flow without the need for manual intervention.
b. Precision and Control: Electric gate valves offer superior precision in controlling fluid flow. The electric actuators enable gradual and accurate adjustments, ensuring optimal performance in various industrial processes.
c. Remote Operation: With electric gate valves, operators can control the valve's operation from a distance, providing flexibility and convenience, especially in large or hazardous environments.
d. Reliability: The automated nature of electric gate valves contributes to increased reliability. Consistent and repeatable valve operation reduces the likelihood of errors and ensures a more reliable fluid control system.
Applications of Electric Gate Valves:
Electric gate valves find applications in diverse industries, including:
a. Oil and Gas: Used in upstream and downstream processes for flow control in pipelines, refineries, and drilling operations.
b. Water Treatment: Employed in water distribution systems, wastewater treatment plants, and desalination facilities.
c. Power Generation: Utilized in power plants for controlling the flow of water, steam, or other fluids in turbines and cooling systems.
d. Chemical Processing: Applied in chemical plants for managing the flow of various chemicals in production processes.
e. Manufacturing: Used in manufacturing processes that require precise control over the flow of fluids in machinery.
Electric gate valves represent a technological advancement in fluid control systems, offering automation, precision, and reliability. Their applications across industries showcase the versatility and efficiency that electric gate valves bring to fluid management processes. As technology continues to evolve, electric gate valves are likely to play an increasingly integral role in optimizing industrial operations and ensuring the seamless regulation of fluid flow.
242
0
0

Comments
All Comments (0)